The power plant market is somewhat of a chess game for stainless steel suppliers. Suppliers should think of their position this way because winning requires analyzing all of the moves from the opposition, while grasping all the strategic options. Then, the next move is supplying a product, which the customer perceives to be the lowest total cost of ownership (LTCO).
By Bob McIlvaine, President & Founder – The McIlvaine Company
Market Turbulence
The power plant and stainless steel markets are more turbulent now than ever before. Nuclear power plants in Germany are being shut down, and there is also a real possibility of tactical or larger nuclear weapons being used on or upwind of Germany.
The importance of net zero in 2050 is also in question, as there is the potential for net zero with just one round of thermonuclear exchanges. Several countries, such as China, have trended away from commitments made in Paris for greenhouse gas reduction. It is hard to say what the U.S. government will choose to do in the future.
Another challenge is the creativity of competitors. There are acquisitions taking place for complementary products, entry into new markets, and expansion into complete solutions.
Markets Will Be Shaped By Life Quality Implications
A winning strategy requires focusing on the most promising technologies. Life quality perceptions will determine which technologies are most promising, and therefore shape the markets of the future.
Most strategies such as net zero in 2050 are pursued without fully assessing several factors, including:
- Life quality enhancement as opposed to life quantity.
- Discounted future value.
- Tribal values.
An example of life quality enhancement, is that some Ukrainians choose to sacrifice their lives in the current disruptive state, because their goal is life quality for the tribe, rather than life quantity.
A clear example of discounted future value is the 100 year initiative for greenhouse gas reduction, versus a nuclear incident now. Lastly, we cannot underestimate the role of tribal values, as many countries and groups operate as a tribe.
It is important to note that life quality and tribal values are interdependent. Most sustainability models are utopian, however the reality is that people choose to support their own life quality values. If their tribal values are not in the best interest of all of humanity, then this will impact the markets.
Power Plant Harm Factors Keep Changing
Another aspect of any power strategy is to continually evaluate the harm calculations. History suggests that as scientific knowledge about an environmental problem grows, the perceptions of harm can vary greatly.
The McIlvaine Company was hired by the EPA to evaluate the mitigation costs of acid rain reduction. The company testified before Senate committees on the subject.
In retrospect, it was found that the entire harm analysis was flawed. Acid rain has not destroyed forests and buildings to the extent predicted. On the other hand, there was complete ignorance about the reaction of SO2 in ambient air to form deadly fine particulates.
The reduction benefits were much greater than anticipated, but for completely different reasons. In the 1980s, dioxins were thought to be so deadly that waste incineration should be avoided. Today, regulations around the world prohibit land filling if the material is combustible.
The potential for the harm perception to change over time is a function of the importance and number of empirical factors in the harm determination. The calculated harm from greenhouse gases has many more empirical factors than any other regulated pollutant. It could turn out that the harm is so great that expensive carbon negative technologies are needed now. The opposite is also possible.
Accordingly, stainless steel suppliers should take this into account. Suppliers and their OEM clients making acquisitions or investing in R&D and marketing also need to evaluate each power option with all of this in mind.
Assessing The Winning Power Plant Technologies
Stainless steel is an important component in the Air, Water, Energy (AWE) market.1 Figure 2 represents annual expenditures for AWE products over the 2022 to 2050 time frame, under two scenarios. One is based on life quality decisions, such as the example of Europe to continue operating coal plants temporarily. The other is the program to achieve zero net carbon emissions by 2050.
Flow includes pumps, valves, fans, compressors, duct, piping, hoses, and couplings. Treat includes scrubbers, filters, combustors, pulverizers, SCR, and treatment chemicals. Solutions includes system design, service, IIO, control valves, hose couplings, and pump variable speed drives.
Not included are construction, foundations, buildings, or any electrical equipment. Figure 3 demonstrates the segmentation by technology.

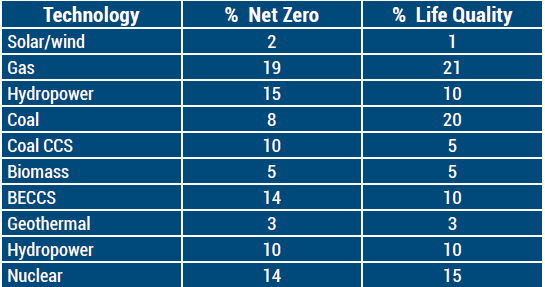
Types of Energy Production
Market share will increase in solar and wind areas, even without credit for carbon neutral aspects. Offshore wind can provide steady and large amounts of power to densely populated coastal areas. The significance to stainless steel suppliers is the negative effect on the market.
By utilizing solar and wind hydrogen, fuel can be created. Uses such as storage favor the approach of eloctrolyzers and green hydrogen. Hydropower and geothermal will both be important, but is limited by available sites. For example, Andritz is generating nearly $1 billion USD in annual revenues for this technology. Hydropower is a limited resource with some environmental challenges, but an important option for reduced CO2.
Ammonia can also be created with CO2 sequestration. Ammonia can be directly combusted or converted to hydrogen prior to combustion. An example is Yara, a major ammonia producer, that has been contracted to provide millions of tons of ammonia to Japanese power plants. The process will sequester CO2 so it can be called ‘blue’ and not ‘grey’. Plenty of severe service stainless steel is used to handle the temperatures and pressures.
Solid fuel fired power plants are the traditional AWE solution, including companies such as Combustion Engineering, Babcock & Wilcox, and Mitsubishi. Several Chinese suppliers have taken advantage of the fact that the majority of new coal fired plants have been built in China. Turbulence in this area will impact Chinese solutions suppliers. Total coal fired capacity has risen to 60% of the peak capacity in the U.S., and solutions licensed from U.S., European, Chinese, and Japanese suppliers are common.
There is a very big potential for biomass combustion with carbon capture and sequestration (BECCS). The Drax model could be duplicated in many countries. The sequence is:
- Install coal fired boilers.
- Progressively co-combust more biomass.
- Fully convert to biomass.
- Install carbon capture and sequestration.
This technology is predicted by The Mcilvaine Company to be utilized to a greater extent than predicted by IEA. This is for a few reasons, including:
- It is the only economic carbon negative option.
- It is the most flexible.
- Costs are lowest initially when operating as a conventional coal plant.
- Many existing coal fired boilers can be slowly upgraded as needed.
- Shutting down coal fired plants and destroying the assets reduces the flexibility for the future.
Conclusion
The power plant market will be a major opportunity for stainless steel suppliers, even if the net zero program is dominant. The life quality scenario will include a somewhat larger opportunity. The aggregate life quality wishes of the world will shape whatever policy is adopted.

Reference
- AWE Markets published by the Mcilvaine Company.



